Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Law & Legal Procedure - Explained Simply
Book Your Free Bankruptcy ConsultationEverything You Need To Know About The Provision Of Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Filing, and how you can benefit from it.
Is it the end of the world if you are neck-deep in debt without sufficient means to repay? Do you know that federal and state bankruptcy laws can help eliminate or manage one’s debts? If not, its time for you to understand how Chapter 7 Bankruptcy deals with such aspects and can be of great help.
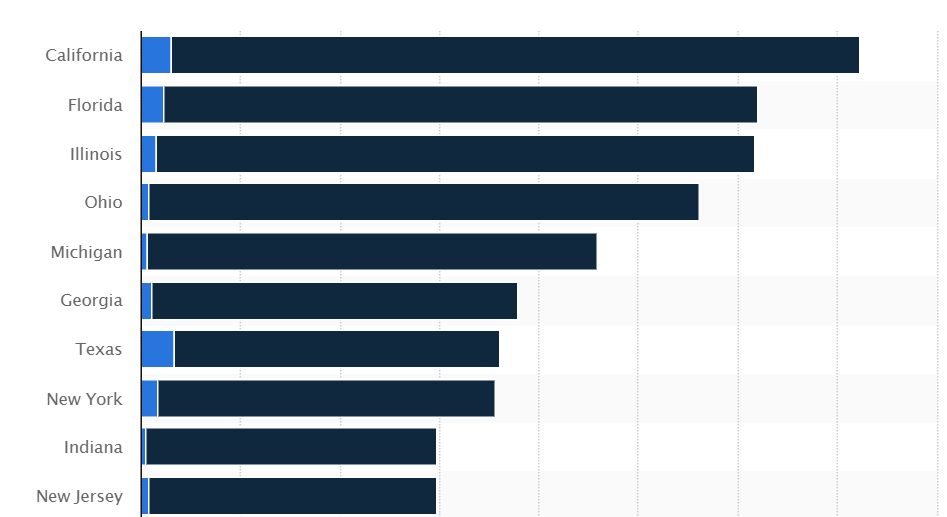
Bankruptcy, in simple words, is a legal process through which individuals or entities who are not able to repay their debts to the creditors may seek relief from the court for some or all of their debts. If the debts become unmanageable, it can have serious consequences and result in eviction from the property or cause severe damage to the credit score. It must be considered as a last resort. According to a recent study, California recorded 36,186 Chapter 7 bankruptcy filings (including a total of 1,518 filed by businesses, and 34,668 non-business filings).
What Is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy is a ‘straight’ or ‘liquidation’ bankruptcy. It can clear off many unsecured debts of a debtor. It is a prevalent type of bankruptcy petition filed in the US. It is a liquidation where the trustee will collect all the assets and will sell any of those assets which are not exempted.
Who Can File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
Any individual, partnership, corporation, or business entity deep in debt can file a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. It provides the opportunity to an honest debtor to make a fresh start. However, there are specific pre-requirements, as mentioned below.
- Individual debtors should undergo credit counselling within 180 days before filing the petition.
- Debtors should pass the means test (applicable to higher-income filers).
- One should not have filed Chapter 7 bankruptcy during the past eight years and Chapter 13 bankruptcy during the last six years.
- If a Chapter 7 or 13 bankruptcy petition has been dismissed, the debtor must wait 181 days before filing the petition again.
- The debtor’s intention should not be to avoid repaying the debt. There should be specific financial compulsions that force them to apply for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
Understanding Some Basic Terminologies Related to Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Once the above information is furnished, the bankruptcy attorney will file the petition with the clerk at the local bankruptcy court by paying a filing fee. However, it is always prudent to understand some basic terminologies related to Chapter 7 bankruptcy:
Credit Counseling
Credit counselling a mandatory process that aims to inform the debtors about available options that they might not be aware of. The counsellor can suggest such alternatives to keep them out of bankruptcy. Every individual debtor filing a Chapter 7 bankruptcy should have undergone it within 180 days before filing the petition.
Means Test
The Means Test calculates whether the debtor can afford to pay at least a meaningful portion of the total debts. The test compares the debtor’s income with the median income for the state. Simultaneously, it compares the debtor’s expenses to what others generally pay for similar commodities in the debtor’s region.
Bankruptcy Trustee
The bankruptcy trustee takes ownership of the debtor’s assets and sells them. The creditors should raise proper claims to receive payment from the proceeds of assets sold by the bankruptcy trustee.
Discharged Debts
The unsecured creditors rarely receive all dues the debtor owes them. It is because there are usually not any assets left for sale after accounting for exempt property to pay anyone. It results in the trustee filing a ‘No Asset’ report with the court. Under such circumstances, the unpaid balances are discharged. These are referred to as discharged debts, and the debtor no longer owes that money to the creditors.
Exempt Property
There could be assets mortgaged as security for the loans taken by the debtor, and the trustee cannot take over all the debtor’s assets. The law permits that the specific exempt property not be stripped of everything one needs. Federal and State Government statutes apply to particular property types. Some of the common exemptions may include:
- Debtor’s house or residence
- Debtor’s vehicle
- Specific retirement benefit accounts
- Any property required for working and earning a living
Creditors Meeting or 341 Meeting
Following a Chapter 7 bankruptcy filing, the court calls a creditor’s meeting, known as the 341 Meeting, to all the creditors listed out in the bankruptcy documents.
- The bankruptcy court judges do not attend this 341 meeting to ensure that they remain impartial.
- The bankruptcy trustee asks several relevant questions to the debtor to confirm if the information supplied in the bankruptcy documents is correct.
- It also determines if the debtor understands the ramifications of filing bankruptcy and receiving a debtor’s discharge.
Debtor’s Discharge
If neither the trustee nor the creditors object on supportable grounds, the bankruptcy court automatically grants a discharge. However, the creditor can file a complaint objecting to the discharge ruling up to 60 days after the 341 meetings. If there is no such complaint, the release takes effect. Thus, the debtor is relieved of the debt. It also prevents the creditors from collecting any debt personally if it arose before the Chapter 7 bankruptcy filing.
How Does The Process For Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Work?
Any person or entity applying for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy has to collect the following financial records before filing the petition.
- Payslips and tax returns
- Bank statements
- Credit Card statements
- Loan documents
Besides, the petitioner has to provide the following information.
- Schedule of assets and liabilities
- Statement of financial affairs
- Listing of all properties, debts, creditors, income, expenses, and other property transfers
- Declaration regarding debtor education, also known as credit counseling
- A pass result of the means test to qualify for filing Chapter 7 bankruptcy
On filing a Chapter 7 bankruptcy petition, the court does the following,
- Place a temporary stay on the debtor’s current debts, which means creditors have to stop collecting payments, evicting them from their property, or turning off their utilities, etc.
- Have legal possession of the debtor’s property and appoint a Bankruptcy Trustee to oversee their case.
Final Words
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy provides the debtor a discharge against specific unsecured debts. The debtor should have low income to qualify for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. The debtor’s non-exempt property can be sold by the bankruptcy trustee to repay the creditors. Filing bankruptcy can have an impact on your credit score too. Though repaying the debts on time will be the best way to go about in life. However, if circumstances force one to default, one has a ray of hope in the form of a Chapter 7 bankruptcy proceeding. Debtors can get a discharge of their debts and make a fresh beginning of their lives.
Reference
California Chapter 7 bankruptcy information
Retrieved from:
http://www.californiabankruptcy.info/chapter7.html
Chapter 7 – Bankruptcy Basics
Retrieved from:
https://www.uscourts.gov/services-forms/bankruptcy/bankruptcy-basics/chapter-7-bankruptcy-basics
What Is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy? (By Louis DeNicola, December 2, 2019 )
https://www.experian.com/blogs/ask-experian/what-is-chapter-7-bankruptcy/