California Bankruptcy Law
Book Your Free Bankruptcy ConsultationA Brief Guide On Getting Out Of Debt Through Chapter 7 Bankruptcy & Chapter 13 Bankruptcy San Diego: Understanding The Difference Between Chapter 7 And Chapter 13 Before You File A Bankruptcy
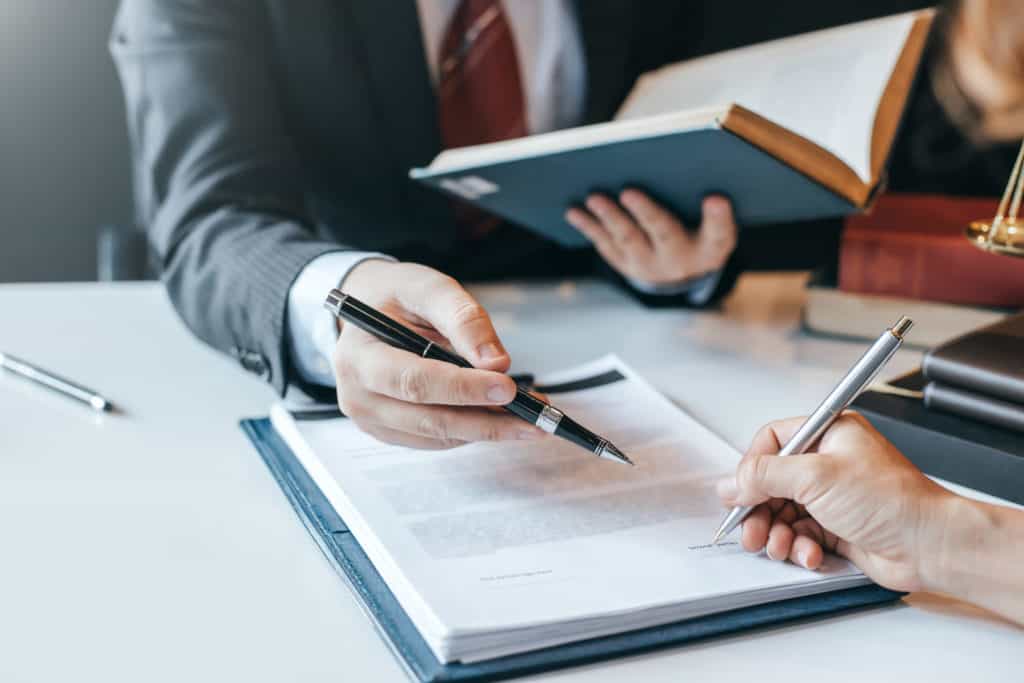
With an overall ailing global economy, there is the closure of businesses and job losses worldwide. It leaves you with a heap of debts to clear in the form of mortgages, car loans, credit card bills, utility payments, and more.
If you are overwhelmed with debts and do not have any solution in sight, rather than losing hope and getting depressed, preparing for bankruptcy could be one of the best options. If you are living in California, you are governed by the California Bankruptcy Law. Let us see the different aspects of Bankruptcy laws and how to prepare for bankruptcy in California.
What You Must Know About California Bankruptcy Law
Bankruptcy in California works differently from that in other states. There are many different types or “chapters” of bankruptcies in California. As an individual, you should be concerned with two types: Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy laws.
Before discussing Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 laws, let us understand the bankruptcy concept. An adequate understanding can help you choose the right option.
Bankruptcy is the legal process that helps debtors get relief from the debts they cannot pay. It is also simultaneously helpful to creditors to get paid from the debtor’s assets or property proceeds. Before filing for bankruptcy, one should know that it does not remove all debt. The debtor cannot discharge certain assets in bankruptcy. Therefore, seeking legal counsel is the right way to make the most of the Bankruptcy laws. As Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 are the most common California Bankruptcy Laws, let us look at the differences between the two.
California Bankruptcy: Chapter 7 And Chapter 13
Laws of both Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy involve individuals. However, there are fundamental differences between the two, as discussed below.
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy also denoted as Liquidation Bankruptcy, allows the debtor to wipe out various debts and make a fresh start. Generally, individuals with large credit card debts and unsecured loans with few assets choose Chapter 7 Bankruptcy. It allows the discharge of various liabilities except for child support, alimony, student loans, specific taxes, and fraudulent debts.
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy is understood as reorganization Bankruptcy because debtors can reschedule their debt payments to manage their current financial crisis. It allows debtors to prevent a house foreclosure or make up for a missed car loan repayment. It also allows one to avoid interest from accruing on one’s tax debt. It is the ideal bankruptcy for those who prefer to retain their secured assets. It proves useful when the debtor has valuable non-exempt property and a steady income source.
An adequate understanding of Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy laws will provide clear guidance in the matter.
Filing Chapter 7 in San Diego : How Does California Bankruptcy Work?
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy law is only for those debtors who are in dire need of debt relief. Hence, one can only qualify for this bankruptcy by satisfying specific conditions.
- If the debtor’s total yearly income is less than the Median Californian Income for a household, they qualify for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy. The Median Californian Income for 2020 is $71,228 for a single household.
- If the income is more than $71,228, the debtor needs to pass the means test to seek protection under Chapter 7 Bankruptcy.
Chapter 7 enables the debtor to discharge all eligible debts. These debts exclude the following.
- Student loans
- Child support and alimony
- Tax debt
- Debts owed for injury caused by DUI
- Restitution following a criminal conviction
After eliminating all eligible debts, the trustee can sell the debtor’s non-exempt assets to pay off the creditors. Some of the exempt assets include:
- Retirement benefits and deferred compensation plans like the 401(k) account
- House claim by the debtor as primary residence up to certain equity limits
- Primary vehicles, if used for business or personal reasons such as transporting the debtor’s children, where other public transportation is not available.
- Household items worth less than $675
Generally, it is found that the debtor does not have any assets left for sale in Chapter 7 Bankruptcy in San Diego. It is the ideal option if a debtor qualifies for it. It is essential to consult a legal expert and avail counselling before filing a Chapter 7 Bankruptcy petition.
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy California : How Does Bankruptcy Work?
Chapter 7 helps settle all eligible debts within a few months, whereas Chapter 13 reorganizes the debt over an extended period.
This bankruptcy envisages the debtor and the trustee to formulate a strategy to pay off all or a percentage of the debt over three to five years. It depends on the kind of debts and the assets of the debtor. According to the agreed plan, the debtor makes a single consolidated payment monthly that a trustee distributes to the creditors.
One of Chapter 13 Bankruptcy’s merits is that it helps catch up on the delayed mortgage and car loan repayments. If there is residual money after paying the secured creditors, it goes towards paying the unsecured creditors. At the end of the plan, the rest of the debts get automatically discharged.
Debtors having property and not wishing to foreclose the mortgage prefer Chapter 13 Bankruptcy. It helps them retain the asset and pay off the debts.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Chapter 7 And Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Laws
Below, we discuss the benefits and drawbacks of both Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy laws.
Advantages Of Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- Debtors get a fresh start after discharging all eligible debts. The debts that remain will be for the secured assets on which the debtor should sign a Reaffirmation Agreement.
- The debtor gets protection against wage garnishment and creditor’s collection efforts from the date of filing.
- Neither the wages the debtor earns nor the property they acquire after the filing date are available to the creditors.
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy does not have any minimum amount of debt.
- The proceedings will be over, and the debts discharged within six months.
Disadvantages Of Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- The debtor loses their non-exempt property as the trustee sells it to repay the creditors.
- There could be secured assets not covered by California Bankruptcy exemptions. In such cases, a Chapter 13 Bankruptcy petition is a better option.
- Co-signers to the loan do not get discharged unless they also file for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy separately.
- Once the debtor files Chapter 7 and gets a discharge of the debts, they cannot do so again for eight years.
Advantages Of Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
- It allows one to retain one’s assets, exempt and non-exempt.
- Though it does not discharge debts fully, the debtor can reduce it under the Chapter 13 repayment plan.
- The debtor gets immediate protection against creditor’s collection efforts and wage garnishments.
- Comparatively, more debts are available for discharge.
- If the Chapter 13 Bankruptcy repayment plan provides full payment, it protects the co-signers from the creditor’s collection efforts.
- Protection is available against foreclosure of the mortgage as long as one adheres to the repayment terms of Chapter 13.
- This bankruptcy provides more time to pay non-dischargeable debts like taxes and child support.
- Repeated filing under Chapter 13 is allowed.
- It provides the debtor with options to separate the creditors by class, where they receive different percentages of payment.
Disadvantages Of Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
- The repayment plan uses the debtor’s post-bankruptcy income to pay back the debt over the period decided by the Chapter 13 rules.
- The debt will continue to last until the end of the term, usually three to five years.
- The legal fees in the case of Chapter 13 Bankruptcy are higher because of the case’s complexity.
- Commodity brokers and stockbrokers are not eligible to file a Chapter 13 Bankruptcy petition.
How Would You Know Which Is Right For You – Chapter 7 Or Chapter 13?
From the above discussion, it is clear that various factors decide which of the two options, Chapter 7 and Chapter 13, is the best for a debtor. The below list summarizes such conditions for both laws.
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy law is the right one for a debtor if they satisfy the following conditions.
- The debtor doesn’t earn sufficient income to repay their creditors.
- The debtor’s income is less than the California Median Income for a similar household.
- The debtor passes a means test when their annual income exceeds the median.
- The debtor doesn’t have non-exempt assets for the trustee to dispose of to repay the creditors.
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy law is ideal under the following circumstances.
- The debtor is not eligible to file for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy for some reason.
- The debtor earns sufficient income to repay the creditors and wishes to retain exempt and non-exempt assets.
- The debtor has a higher percentage of secured debts making Chapter 13 Bankruptcy a better choice.
California Bankruptcy Exemptions
As mentioned in the discussion so far, various California Bankruptcy exemptions are available when filing a Chapter 7 Bankruptcy petition.
California Bankruptcy exemptions are of two types, as discussed below.
System 1: It comprises the following.
Homestead
Denotes real estate property, including a mobile home, boat, or a community apartment subject to the following limits.
- $75,000 if single and not disabled
- $150,000 for families where no other member has a homestead
- $175,000 if older than 65 years or disabled in some way
Personal Property
It includes the following assets
- Appliances, clothing, furniture, jewelry, etc.
- Health aids
- Bank deposits up to $2,000 from Social Security Administration ($3,000 for a married couple)
- Motor vehicles up to $1,900
Insurance
It includes different insurance types like disability or health benefits, married life insurance benefits, the unmatured life insurance policy loan up to $8,000, fidelity bonds, homeowner’s insurance, fraternal unemployment benefits, etc.
Miscellaneous
It includes business or professional licenses, business partnership properties, and inmates’ trust funds up to $1,000.
- Pensions – Includes all retirement benefits.
- Public Benefits – includes unemployment benefits, financial aid to students, relocation benefits, etc.
- Trade Tools – comprise of tools used in business/trade up to a maximum of $5,000
- Wages – A minimum of 75% of wages
System 2: It consists of the following.
Homestead
Personal property used as residence up to $17,425
Personal Property
- Animals, crops, furnishings, appliances, household goods, clothing, musical instruments, and books up to $450 per item
- Burial plot up to $17,425 instead of the homestead
- Health aids
- Jewelry up to $1,150
- Motor vehicles up to $2,775
- Personal injury recoveries up to $ 17,425
Insurance
Disability benefits, unmatured life insurance policy, life insurance proceeds for family support, and unmatured life insurance contract up to $9,300
Miscellaneous
Alimony and child support
Pensions
ERISA qualified benefits necessary for the support
Public benefits
include crime victim compensation, social security, unemployment compensation, veteran’s benefits, etc.
Trade Tools
All trade tools up to $1,750
Wages
None
Wildcard
It includes an amount of $925 of any property plus the unused portion of homestead or the burial exemption of any property.
How To File For Bankruptcy In San Diego?
On deciding the right chapter, the debtor can prepare for filing the petition by adhering to the following procedure.
Gather the requisite documents such as
- Identification
- List of all bank accounts and insurance policies
- Tax returns filed within the last two years
- Proof of ownership of the asset
- Income proof for the past six months
It is mandatory to attend a credit counseling session through a court-approved service.
Consult bankruptcy attorney in San Diego who will file the petition for you.
Final Words
Filing for bankruptcy in California is a complex process. It is the last resort for someone who is in the dire need of debt relief. If you are a debtor struggling to repay your debts, you can file the petition under Chapter 7 or Chapter 13. However, which one is right depends on your eligibility, and unique situation. Hence, it is advisable to consult an experienced bankruptcy lawyer San Diego CA who can guide you through the entire process.